AGE-RELATED MACULAR DEGENERATION
Important cause of blindness:
- Diabetes and its effects on the retina is the most frequent cause of blindness in the active population (20 to 74 years).
- At the time of diagnosis of Diabetes, up to 20% of patients show signs of Diabetic Retinopathy. At 15 years of diagnosis, 50% present it.
- In patients with Type 1 Diabetes with more than 30 years of evolution, 100% of the patients show signs of Diabetic Retinopathy.
Chronic Vascular and Neurological Impairment:
Diabetes produces an alteration in the normal vascularization of the retina causing fluid leaks (macular edema) and sometimes, causes blood vessels to grow abnormally causing haemorrhages (proliferative diabetic retinopathy). Therefore, such chronic damage to ocular tissues can lead to vascular and neurological failure of the eye, with the presence of extensive areas of ischemia (lack of blood supply) and inflammation.
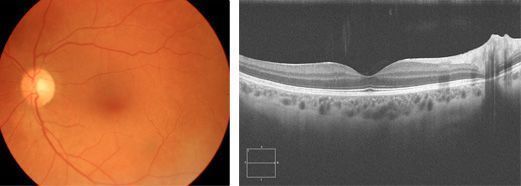
Healthy retina without vascular damage. Normal tissue thickness in the OCT scanner.
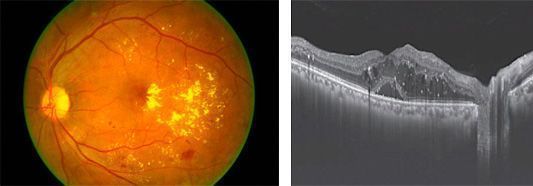
Retina with secondary changes to Diabetes. It shows the presence of retinal haemorrhages, capillary micro aneurysms and exudation due to vascular extravasation (macular edema). The OCT scanner shows thickened and destructured retina
Symptoms of Diabetic Retinopathy:
- Blurred vision: Reduction of the central vision (distance vision and reading ability are reduced).
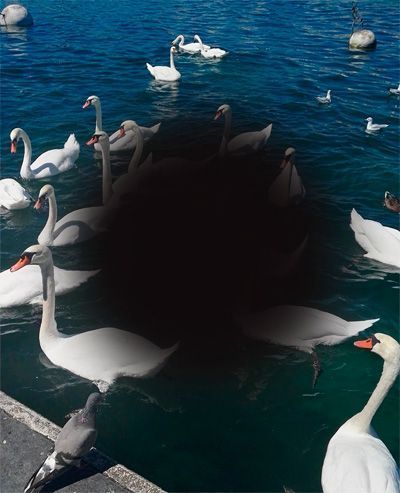

- Distorted Vision: Straight lines are perceived as being undulated.
- Vision of spots: Internal bleedings in the eye (vitreous haemorrhages) can cause the appearance of spots that obscure vision partially and even totally in some cases.
Early diagnosis:
- Periodic visits to the Ophthalmologist: patients affected by Diabetes should make periodic visits even when there are no symptoms.
- Self-assessment is essential: with the help of various tools recommended by your ophthalmologist, patients should periodically observe the quality and quantity of their vision and visit the ophthalmologist if necessary
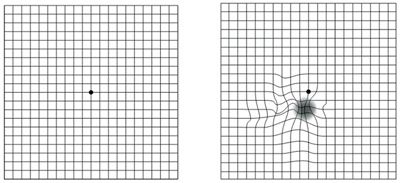
Amsler grid, recommended for the self-assessment of distortion in central vision, affected in Macula Diseases.
Diagnostic Tests: OUR TECHNOLOGY
In PRESBIT we have the most advanced technology for the Early Diagnosis and Treatment of the different complications of Diabetic Retinopathy.
The OCT scanner (Optical Coherence Tomography), Fundus Autofluorescence, Colour Retinography, Fluorescein Angiography, Microperimetry, Multifocal Electroretinogram (ERGm) and Ocular Ultrasound will allow the correct diagnosis and monitoring of the different stages of the disease.
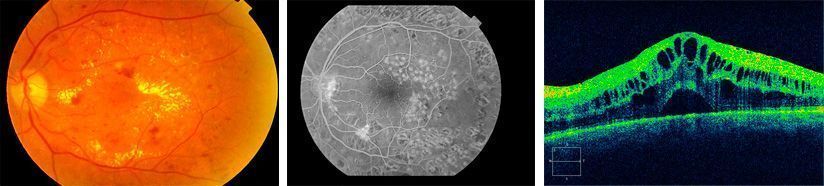
Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy:
Intravitreal Antiangiogenic Therapy: (Anti-VEGF), intravitreal injections of corticoids and laser of the retina are the treatments that are combined in the management of diabetic retinopathy.

Intravitreal Injection Technique
Laser Treatment: It is sometimes used to improve the control of the disease, allowing sclerosis of focal vascular lesions that produce macular edema, and ablation of ischemic areas in the retina.
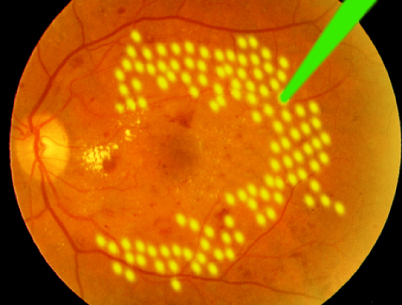
Photocoagulation Procedure with Argon Laser
Surgery: The need to perform vitreoretinal surgery for the treatment of haemorrhagic and fractional complications of Diabetic Retinopathy is frequent.
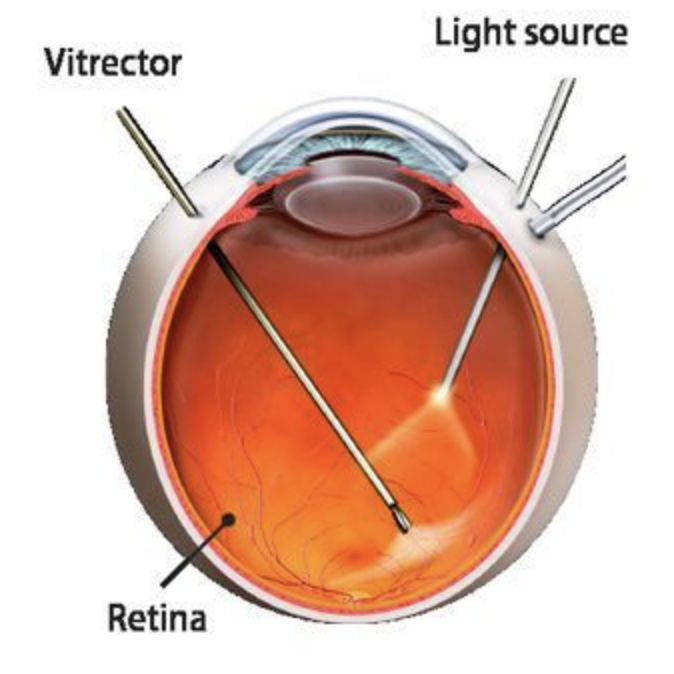
Vitrectomy surgery.
Our Retina Expert, Dr Luis Amselem Gómez:
“Diagnosis and Early Treatment in Diabetic Retinopathy is very important. Identifying patients at risk and establishing a prevention and monitoring guideline helps prevent blindness caused by the disease.”
Let’s be decisive with Diabetic Retinopathy, it is a fight we can now win.


