REFRACTIVE SURGERY
What is refractive surgery?
Refractive surgery is a set of surgical procedures that modify the anatomy of the eye, especially the cornea, eliminating the refractive defects of myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism so that the use of glasses or contact lenses is not necessary.
In a first visit the ophthalmologist will evaluate the characteristics of the patient to decide if he or she is suitable to undergo the surgery and what the ideal treatment for their pathology is.
There are several types of refractive surgery:
– Laser surgery (PRK, LASIK, LASEK)
– Surgery with intraocular lens.
This type of intervention does not require hospital admission. Topical anaesthesia (drops) is used and its duration is approximately 15 minutes. The vision can be blurry in the first hours of the post-operative period, but clarity is recovered throughout the day and the visual capacity progressively improves with the passing days.
MYOPIA
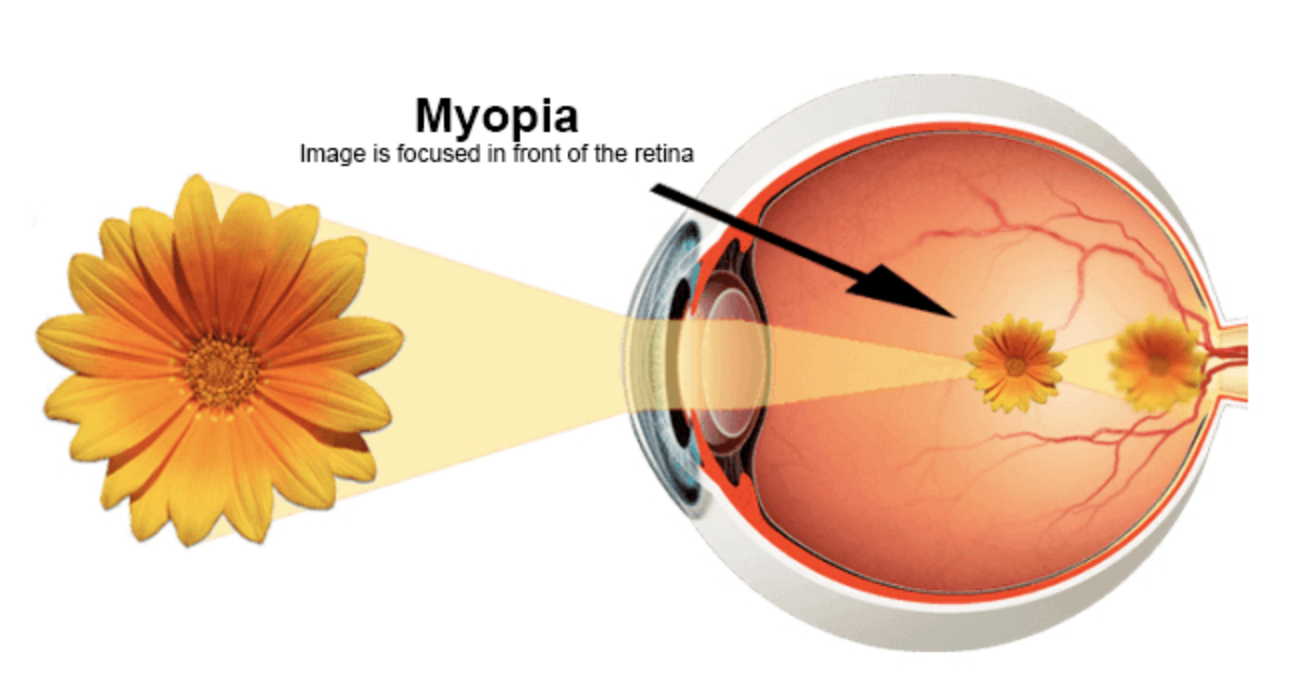
Myopia is a problem of refraction of the eye. It manifests itself when the patient notices distant objects as being blurred. This is due to an excessive curvature of the cornea or an excessively elongated eyeball that causes the images of the objects to form before reaching the retina.
The symptoms of myopia can appear from childhood and may increase over time, but this usually stabilizes in early adulthood.
SYMPTOMS
· Need to squint eyes to see distant objects or have to approach them to see them clearly.
· Visual fatigue.
· Headaches.
HOW IS IT CORRECTED?
Myopia can be corrected with glasses or contact lenses, but if a myopic person wants to stop using glasses, there are several surgical options: laser refractive surgery through different techniques or the implantation of an intraocular lens.
DID YOU KNOW?
Myopia affects one in three Spaniards. It is the most common visual defect among those under 45 years of age.
HYPEROPIA
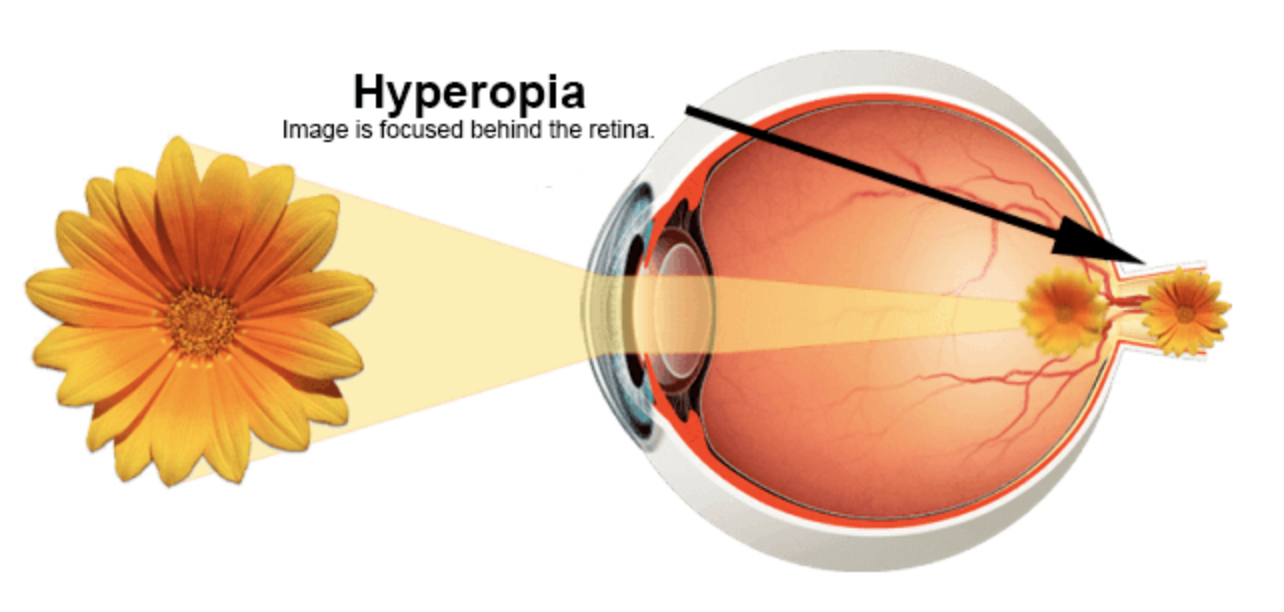
Hyperopia is an anomaly or defect of the eye that causes blurry vision, although, at a certain age, there is a difficulty to see clearly distant objects too.
An eye that is able to correctly focus the images on the retina is called an emmetropic eye. In hyperopia, the eye has a shorter length than an emmetropic eye or a cornea that is flatter than normal and therefore the images of distant objects are focused behind the retina. For example, watching television can be a problem, but reading a highway sign is probably not. It is the opposite of myopia.
SYMPTOMS
- Blurry close objects. As the condition worsens, objects at all distances may be blurry.
- Visual fatigue
- Headache.
- Difficulty to concentrate and maintain a clear vision during reading.
- Red eyes
HOW IS IT CORRECTED?
The correction of hyperopia is more complex than that of myopia. This depends on age, the degree of hyperopia, and above all, the symptoms. It is corrected with glasses or contact lenses, but also by corneal surgery with excimer-femtosecond lasers or with phakic lenses, which are lenses that are placed between the cornea and the lens.
ASTIGMATISM
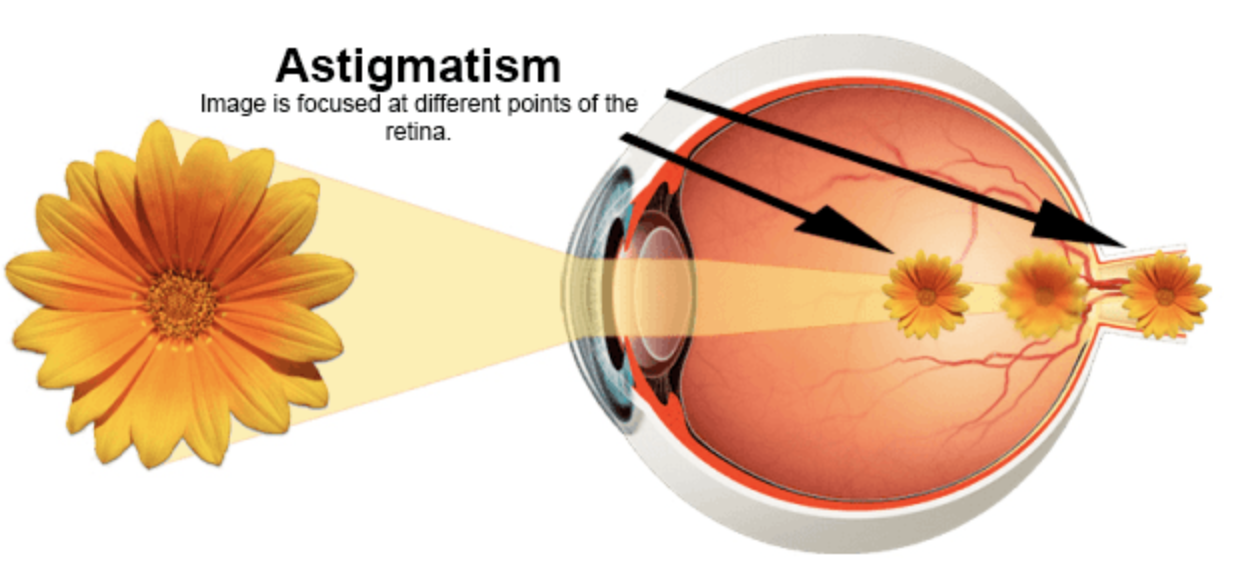
Astigmatism is an anomaly or defect of the eye that consists of an irregular curvature of the cornea or the shape of the eye’s lens. As a result, the vision for both near and distant objects appears blurry or distorted.
SYMPTOMS
- Headaches.
- Visual fatigue.
- Need to squint eyes to see clearly
- Distorted or blurred vision at any distance.
- Difficulty driving at night.
HOW IS IT CORRECTED?
Astigmatism can be corrected with glasses, contact lenses and surgery. The purpose of refractive surgery is to permanently change the shape of the cornea. This change in the shape of the eyes restores the ability to focus. There are many types of refractive surgeries and a visit to an ophthalmologist can help decide if surgery is a good option.
Say goodbye to myopia, hyperopia and astigmatism. Get total freedom for your eyes.
CONTACT US. FREE FIRST INFORMATIVE VISIT
Financing in 12 months without interest.


