UVEITIS
What is Uveitis?
Uveitis is an inflammation of the uvea, which is a membrane that surrounds the inside of the eye, formed by the iris, the ciliary body and the choroid, which together form the middle layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera (white part of the eye).
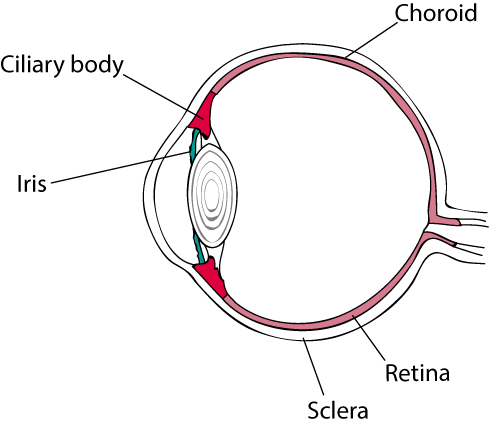
Types of uveitis
There are several types of uveitis, which are defined based on the part of the eye primarily affected.
- Anterior uveitis or Iridocyclitis is an inflammation of the anterior uvea (iris, ciliary body)
- Intermediate uveitis or Pars Planitis is an inflammation of the pars plana, a narrow area located between the iris and the choroid.
- Posterior uveitis or Choroiditis is an inflammation of the posterior uvea (choroid).
- Pan uveitis is the inflammation of all layers of the uvea.
Causes
It can be caused by infections, systemic diseases, toxins, traumas and other causes, although in many cases the etiology is unknown.
Symptom
- Redness of the eye
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light (photophobia)
- Floaters
- Pain that can be moderate or intense
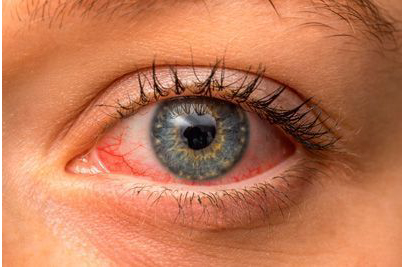
Uveitis can be associated with a high incidence of complications that can put vision at risk such as cataracts, retinal detachment, intraocular haemorrhages, glaucoma or fluid in the central region of the retina (macular edema). Hence the importance of the assessment and control by an ophthalmologist.
Treatment
The treatment can be very varied (drops, oral or systemic medication, injections, surgery) depending on the cause, the time of evolution and severity.


